더보기
52일 차 회고.
어제 강의실에 자격증 책을 두고 가는 바람에 집에서 공부를 하지 못했다. 그래서 오늘 공부를 좀 더 많이 할 예정이다. 그리고 어제 우리 강의실에서 코딩테스트 시험이 있었는데 자리를 치우지 않고 가서 다음부터는 노트북을 사물함에 넣어두고 가야겠다.
1. Transformer
1-1. Model
Transformer
- transformers.models
- Transformer 기반 모델을 PyTorch 및 TensorFlow로 구현한 모듈이다.
- 각 모델에 맞는 Tokenizer도 함께 제공되며, AutoModel 및 AutoTokenizer 클래스를 활용하면 특정 모델에 맞는 적절한 모듈을 자동으로 불러올 수 있다.
- transformers.pipeline
- Pre-Trained 모델을 활용하여 다양한 Task를 수행할 수 있도록 제공하는 추론 API이다.
- transformers.Trainer
- Pre-Trained 모델을 특정 Task에 맞게 Fine-Tuning할 수 있도록 도와주는 학습 및 평가 모듈이다.
Transformer 학습 방법
- Causal Language Modeling
- 문장 내에서 이전 n개의 단어를 보고 다음 단어를 예측한다.
- Autoregressive 모델이며, 오른쪽으로 단어를 순차적으로 예측하기 때문에 미래의 단어를 볼 수 없다.
- ex. GPT, ChatGPT, GPT-4, LLaMA 등
- Masked Language Modeling
- 문장 내에서 일부 단어를 마스킹하고, 이를 예측한다.
- Bidirectional 모델이기 때문에 문장의 앞뒤 문맥을 모두 활용할 수 있다.
- ex. BERT, RoBERTa, ALBERT 등
- Pre-Training
- Transformer 모델의 가중치를 랜덤하게 초기화한 후, 방대한 데이터셋을 통해 기본적인 언어 능력을 학습한다.
- 학습된 모델은 특정 Task에 대한 지식이없지만, 문법과 일반적인 문장 구조를 이해할 수 있다.
- Fine-Tuning
- Pre-Trained 모델을 가져와 특정 Task에 맞게 추가 학습을 한다.
Transformer Model
- ALBERT - Encoder Model
- 문장 분류(Sentence Classification) / 개체명 인식(Named-Entity Recognition) / 추출형 질의응답(Extractive Question Answering)
# 텍스트 분류
import torch
from transformers import AlbertForSequenceClassification, AutoTokenizer
model = AlbertForSequenceClassification.from_pretrained('textattack/albert-base-v2-imdb')
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('textattack/albert-base-v2-imdb')
inputs = tokenizer('Hello, my dog is cute', return_tensors='pt')
with torch.no_grad():
logits = model(**inputs).logits
predicted_class_id = logits.argmax().item()
model.config.id2label[predicted_class_id]# 토큰 분류
import torch
from transformers import AlbertForTokenClassification, AutoTokenizer
model = AlbertForTokenClassification.from_pretrained('albert/albert-base-v2')
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('albert/albert-base-v2')
inputs = tokenizer(
'HuggingFace is a company based in Paris and New York',
add_special_tokens=False,
return_tensors='pt'
)
with torch.no_grad():
logits = model(**inputs).logits
predicted_token_class_ids = logits.argmax(-1)
predicted_tokens_classes = [model.config.id2label[t.item()] for t in predicted_token_class_ids[0]]# Fill Mask
import torch
from transformers import AlbertForMaskedLM, AutoTokenizer
model = AlbertForTokenClassification.from_pretrained('albert/albert-base-v2')
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('albert/albert-base-v2')
inputs = tokenizer('The capital of [MASK] is Paris.', return_tensors='pt')
with torch.no_grad():
logits = model(**inputs).logits
mask_token_index = (inputs.input_ids == tokenizer.mask_token_id)[0].nonzero(as_tuple=True)[0]
predicted_token_id = logits[0, mask_token_index].argmax(axis=-1)
print(tokenizer.decode(predicted_token_id))# Question Answering
import torch
from transformers import AlbertForQuestionAnswering, AutoTokenizer
model = AlbertForQuestionAnswering.from_pretrained('twmkn9/albert-base-v2-squad2')
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('twmkn9/albert-base-v2-squad2')
question = 'Who was Jim Henson?'
text = 'Jim Henson was a nice puppet'
inputs = tokenizer(question, text, return_tensors='pt')
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(**inputs)
answer_start_index = outputs.start_logits.argmax()
answer_end_index = outputs.end_logits.argmax()
predict_answer_tokens = inputs.input_ids[0, answer_start_index:answer_end_index+1]
print(tokenizer.decode(predict_answer_tokens, skip_special_tokens=True))- GPT - Decoder Model
- 텍스트 생성(Text Generation)
import torch
from transformers import AutoModelForCausalLM, AutoTokenizer
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
model = AutoModelForCausalLM.from_pretrained('gpt2', pad_token_id=tokenizer.eos_token_id).to(device)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('gpt2')
model_inputs = tokenizer('I enjoy walking with my cute dog', return_tensors='pt').to(device)# Greedy Search
# - 현재 시점에서 확률이 가장 높은 단어를 선택하는 방식
greedy_output = model.generate(**model_inputs, maxx_new_tokens=40)
print(tokenizer.decode(greedy_output[0], skip_special_tokens=True))# Beam Search
# 여러 개의 후보(Beam)를 고려하여 최적의 문장을 찾아가는 방식
beam_output = model.generate(
**model_inputs,
max_new_tokens=40,
num_beams=5,
early_stopping=True
)
print(tokenizer.decode(beam_output[0], skip_special_tokens=True))# N-gram 패널티
# - 이미 생성된 단어 시퀀스와 동일한 N-gram이 다시 등장할 경우, 해당 후보의 확률을 낮추거나 제외하는 방법
beam_output = model.generate(
**model_inputs,
max_new_tokens=40,
num_beams=5,
no_repeat_ngram_size=2,
early_stopping=True
)
print(tokenizer.decode(beam_output[0], skip_special_tokens=True))# Top-k
# - 확률이 높은 k개의 단어들을 선택하여 그 중 하나를 랜덤하게 선택하는 방법
set_seed(42)
sample_output = model.generate(
**model_inputs,
max_new_tokens=40,
do_sample=True,
top_k=50
)
print(tokenizer.decode(sample_output[0], skip_special_tokens=True))# Top-p
# - 확률의 합이 p 이상인 단어들을 선택하여 그 중 하나를 랜덤하게 선택하는 방법
set_seed(42)
sample_output = model.generate(
**model_inputs,
max_new_tokens=40,
do_sample=True,
top_p=0.92
top_k=0
)
print(tokenizer.decode(sample_output[0], skip_special_tokens=True))- BART - Encoder-Decoder Model
- 요약(Summarization) / 번역(Translation) / 생성형 질의응답(Generative Question Answering)
# 토큰화
from transformers import BartTokenizer
tokenizer = BartTokenizer.from_pretrained('facebook/bart-base')
tokenizer('Hello World')# 요약
from transformers import BartForConditionalGeneration, AutoTokenizer
model = BartForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained('facebook/bart-base')
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('facebook/bart-base')
ARTICLE_TO_SUMMARIZE = ('')
inputs = tokenizer([ARTICLE_TO_SUMMARIZE], max_length=1024, return_tensors='pt')
summary_ids = model.generate(inputs['input_ids'], num_beams=2, min_length=0, max_length=20)
print(tokenizer.batch_decode(summary_ids, skip_special_tokens=True, clean_up_tokenization_spaces=False)[0])# Fill Mask
from transformers import BartForConditionalGeneration, AutoTokenizer
model = BartForConditionalGeneration.from_pretrained('facebook/bart-base')
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('facebook/bart-base')
TXT = My friends are <mask> but they eat too many carbs.'
inputs = tokenizer([TXT], return_tensors='pt')
input_ids = inputs['input_ids']
logits = model(input_ids).logits
masked_index = (input_ids[0] == tokenizer.mask_token_id).nonzero().item()
probs = logits[0, masked_index].softmax(dim=0)
values, predictions = probs.topk(5)
print(tokenizer.decode(predictions).split())# Question Answering
import torch
from transformers import BartForQuestionAnswering, AutoTokenizer
model = BartForQuestionAnswering.from_pretrained('valhalla/bart-large-finetuned-squadv1')
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained('valhalla/bart-large-finetuned-squadv1')
question = 'Who was Jim Henson?'
text = 'Jim Henson was a nice puppet'
inputs = tokenizer(question, text, return_tensors='pt')
with torch.no_grad():
outputs = model(**inputs)
answer_start_index = outputs.start_logits.argmax()
answer_end_index = outputs.end_logits.argmax()
predict_answer_tokens = inputs.input_ids[0, answer_start_index:answer_end_index+1]
print(tokenizer.decode(predict_answer_tokens, skip_special_tokens=True))
Transformer Task
- Text Classification
- Token Classification
- Question Answering
- Causal Language Modeling
- Masked Language Modeling
- Translation
- Summarization
- Multiple Choice
1-2. Pipeline
Pipeline 내부 프로세스
- Tokenizer
- Tokenization
- 텍스트를 모델이 이해할 수 있는 토큰으로 분할한다.
- ex. 단어 기반 토큰화(Word-based Tokenization)
- Encoding
- Tokenization
- Model
- 입력된 데이터를 처리하고 예측을 수행한다.
- Pre-Trained 모델을 사용하여 자연어 처리(NLP) Task를 수행한다.
- Post Processing
- 모델의 출력을 실제 사용 가능한 형태로 변환한다.
- Decoding
- 모델의 출력을 실제 사용 가능한 형태로 변환한다.
Pipeline
- 특징 추출(Feature Extraction)
import numpy as np
from transformers import pipeline
pipe = pipeline(task='feature-extraction')
pipe('hello')- Fill Mask
import numpy as np
from transformers import pipeline
pipe = pipeline(task='fill-mask', model='distilbert/distilroberta-base')
pipe('The Milky Way is a <mask> galaxy.', top_k=3)- 개체명 인식(NER; Named Entity Recognition)
import numpy as np
from transformers import pipeline
pipe = pipeline('ner', model='distilbert/distilbert-base-uncased', grouped_entities=True)
pipe('The Golden State Warriors are an American professional basketball team based in San Francisco.')- 질의응답(Question Answering)
import numpy as np
from transformers import pipeline
pipe = pipeline(task='question-answering', model='klue/roberta-base')
pipe(
question='베토벤이 태어난 곳은 어디인가요?',
context='루트비히 판 베토벤은 독일의 서양 고전 음악 작곡가이자 피아니스트이다..'
)- 감정 분석(Sentiment Analysis)
from transformers import pipeline
pipe = pipeline('sentiment-analysis')
pipe(['I am King in the world'])- 요약(Summarization)
from transformers import pipeline
pipe = pipeline('summarization')
pipe('''
''')- 텍스트 생성(Text Generation)
from transformers import pipeline
pipe = pipeline('text-generation', model='skt/kogpt2-base-v2', max_length=30)
pipe('나는 오늘 아침에 눈을 뜨고')- 번역(Translation)
from transformers import pipeline
pipe = pipeline('translation', model='circulus/kobart-trans-ko-en-v2')
pipe('오늘 점심으로 파스타를 먹었습니다.')- 제로샷 분류(Zero-Shot Classification)
from transformers import pipeline
pipe = pipeline('zero-shot-classification', model='hyunwoongko/kobart')
pipe(
'개구리는 양서류이다.',
candidate_labels=['교육', '정치', '사업']
)
2. LLM 프로젝트
2-1. Flow Chart
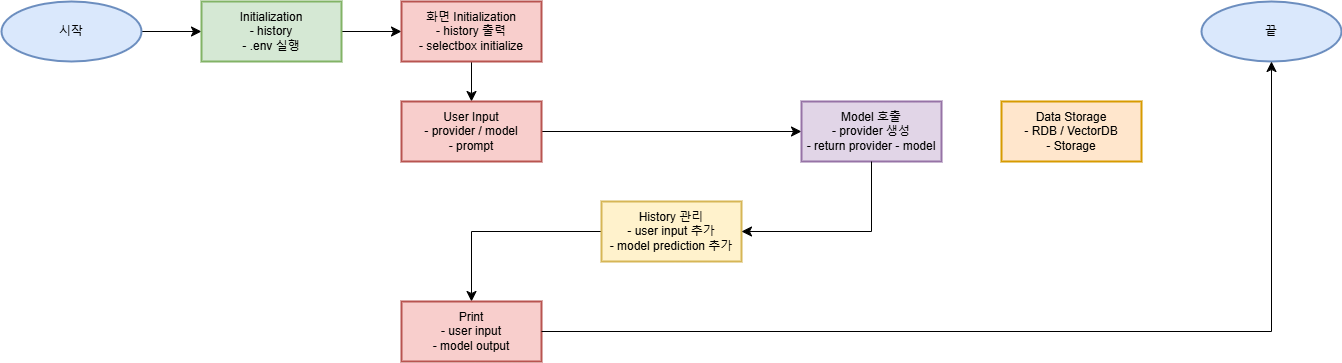
2-2. File Constructure
LLM_PROJECT
├─ .venv
├─ common
│ ├─ database
│ ├─ display
│ │ ├─ constant.py
│ │ ├─ history.py
│ │ ├─ input.py
│ │ ├─ output.py
│ │ └─ utils.py
│ └─ model
│ ├─ groq.py
│ ├─ ollama.py
│ ├─ openai.py
│ └─ provider.py
├─ .env
├─ .gitignore
├─ chatbot.py
├─ README.md
├─ requirements.txt
└─ test.ipynb
2-3. 개발 내용
파일 구조 정리
- Powershell
ollama run gemma3:1b
'SK네트웍스 Family AI캠프 10기 > Daily 회고' 카테고리의 다른 글
| 54일차. Hugging Face - SFT Trainer & LLM 프로젝트 (0) | 2025.03.28 |
|---|---|
| 53일차. Hugging Face - Transformer Trainer & LLM 프로젝트 (0) | 2025.03.27 |
| 51일차. LLM - LLaMA & Claude & SciSpace & LLM 프로젝트 (0) | 2025.03.25 |
| 50일차. LLM - LLM 프로젝트(Chatbot) (0) | 2025.03.24 |
| 49일차. Huggingface - Diffusers & 자연어 딥러닝 - Text2Image & uv & LLM - OpenAI (0) | 2025.03.21 |



